As mentioned in Section 2.1, when any problem dimension
(eg., M, N, or K) is not a multiple of 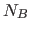 , ATLAS
must call cleanup code to handle the remainder. When the user-contributed
kernel is only modestly faster than ATLAS's generated kernel, letting
the generated code handle cleanup will probably be an adequate solution.
However, when the user-contributed kernel is much faster than the generated
code, using the generated cleanup may represent a significant performance
drop for many problem sizes (see Section 2.7.5 for an
analysis of the cost of cleanup), and thus it becomes necessary for the user
to supply ATLAS with cleanup code as well. In order to understand how
this is done, it is necessary to discuss how ATLAS does cleanup.
, ATLAS
must call cleanup code to handle the remainder. When the user-contributed
kernel is only modestly faster than ATLAS's generated kernel, letting
the generated code handle cleanup will probably be an adequate solution.
However, when the user-contributed kernel is much faster than the generated
code, using the generated cleanup may represent a significant performance
drop for many problem sizes (see Section 2.7.5 for an
analysis of the cost of cleanup), and thus it becomes necessary for the user
to supply ATLAS with cleanup code as well. In order to understand how
this is done, it is necessary to discuss how ATLAS does cleanup.
Subsections
Clint Whaley
2012-07-10